Unlocking the Psychology of a Market Cycle: Insights for Real Estate Agents
How does emotion drive the ebbs and flows of financial markets? It’s a question at the heart of every investor’s strategies. This article demystifies the psychology of a market cycle, revealing how the collective mood swings from greed to fear can create the conditions for boom and bust. Dive into an analysis of the emotional currents that underpin market movements, and learn how to navigate them to make more informed investment choices.
Key Takeaways
Market cycles are driven by emotional responses of fear and greed, leading to price fluctuations and influencing investor behavior such as overconfidence, herd mentality, and biased decision-making.
Market cycles consist of four psychological phases: Accumulation (cautious optimism), Markup (euphoria and FOMO), Distribution (uncertainty and indecision), and Markdown (panic and despair); understanding these emotional states is crucial for informed investing.
Investors can benefit from using sentiment analysis tools and technical indicators to monitor market psychology and employing strategies like developing long-term investment plans and practicing emotional discipline to navigate market cycles effectively.
The Emotional Rollercoaster of Market Cycles

Market cycles are a fundamental aspect of financial markets, including the cryptocurrency market. Understanding crypto market cycles can provide valuable insights into the bull and bear markets, each with its characteristics and market behavior. The bull market is characterized by price surges, while the bear market features declining prices. However, these cycles are not merely about price fluctuations. They are deeply intertwined with human emotions, particularly fear and greed, which significantly influence market movements and investor behavior.
Market sentiment in financial markets is largely driven by two primary emotions, fear and greed. When fear dominates, investors tend to sell their holdings, pushing prices down and affecting the market value. Conversely, when greed takes over, investors enter the market in droves, creating a buying frenzy that drives prices up. These emotional responses to market conditions underline the importance of understanding market psychology for investors.
The Role of Fear and Greed
Investor behavior throughout market cycles is significantly impacted by the emotions of fear and greed. Fear often drives asset prices lower, especially when losses persist over a prolonged period. On the other hand, greed can inflate asset values as investors, driven by aspirations of high returns, exhibit an insatiable appetite for buying. This constant tug-of-war between fear and greed creates the cyclical nature of financial markets.
Market bubbles and crashes can also be fueled by these emotions. Greed can drive prices above their intrinsic value, creating an asset bubble. Conversely, fear can lead to prolonged sell-offs, depressing prices below their fundamental levels due to market overreactions. An understanding of these emotional triggers can guide investors towards more informed decisions, thereby benefiting their investment portfolios.
Emotional Biases Affecting Investment Decisions
Beyond fear and greed, several other emotional biases can influence investor behavior, particularly during a bear market. These include:
Overconfidence bias: leads investors to believe they know more than they do, causing them to take on more risk than they should.
Loss aversion bias: drives investors to sell winning stocks too early due to the fear of a price drop and hold onto losing stocks in the hope of recovery.
Herding bias: causes investors to follow the crowd and make decisions based on what others are doing, rather than their own analysis.
Confirmation bias: leads investors to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts them.
Understanding these biases can help investors make more rational decisions and avoid common pitfalls during an upcoming bear market, as well as in the current bear market.
Even institutional investors aren’t spared from these biases. Emotional biases can lead to suboptimal investment decisions and contribute to market volatility. A detailed understanding and recognition of these biases can guide investors towards more informed decisions, resulting in improved investment outcomes.
Four Phases of a Market Cycle: A Psychological Perspective
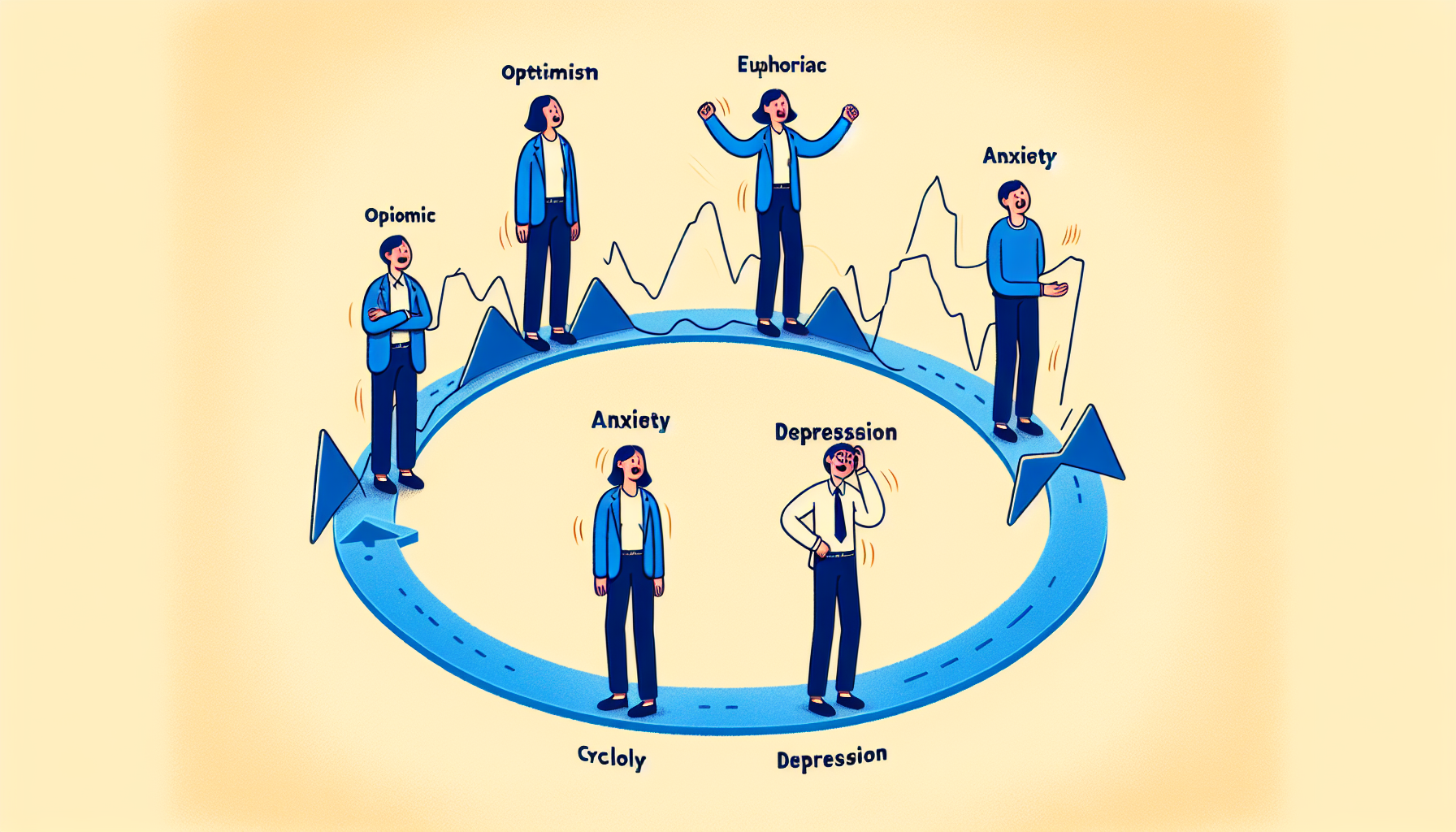
Understanding the four phases of a market cycle from a psychological perspective can help investors navigate market fluctuations more effectively. The market cycle consists of four phases:
Accumulation
Markup
Distribution
Markdown
These phases are essential for understanding market behavior and making informed investment decisions. Each phase is characterized by distinct investor emotions and behavior, which influence market behavior and price movements.
The emotional shifts in the market cycle are as follows:
The accumulation phase is marked by cautious optimism
The markup phase is marked by euphoria and FOMO (fear of missing out)
The distribution phase is marked by uncertainty and indecision
The markdown phase is marked by panic and despair
These emotional shifts reflect the cyclical nature of financial markets and provide valuable insights into market psychology.
Accumulation Phase: Cautious Optimism
The accumulation phase is characterized by:
Cautious optimism among investors
Institutional investors starting to buy significant portions of a particular asset
Recognition of the opportunity to acquire undervalued assets
Requiring patience and the ability to see beyond existing market pessimism
Astute investors often take advantage of this phase to enter the market at lower prices. The sentiment during this phase is often skeptical, but as positive news begins to trickle in, investor interest grows, and prices start to rise. The cautious optimism during this phase sets the stage for the next phase of the cycle – the markup phase.
Markup Phase: Euphoria and FOMO
Following the accumulation phase, the market enters the markup phase, characterized by a sustained uptrend in prices. This phase is often marked by:
Euphoria
Fear of missing out (FOMO)
Overly optimistic investors
Surge in demand from buyers
Higher prices
Overvaluation
As prices continue to rise, more and more traders enter the market, hoping to capitalize on the upward trend. The fear of missing out on potential profits drives buying behavior, with many investors jumping on the bandwagon without thorough analysis or consideration of the asset’s intrinsic value. This irrational exuberance can inflate asset prices beyond their actual worth, setting the stage for the next phase – the distribution phase.
Distribution Phase: Uncertainty and Indecision
The distribution phase represents a period of market consolidation that follows the markup phase. During this phase, prices often move sideways, and market sentiment shifts from bullish to mixed. The euphoria that characterized the markup phase gives way to uncertainty and indecision, as investors struggle to determine the future direction of the market. Distribution phase marks the transition from a bullish to a mixed market sentiment.
During the distribution phase, the market becomes increasingly volatile, with prices fluctuating wildly. Investors who entered the market late during the markup phase start to panic, selling their positions to avoid further losses. This sell-off marks the beginning of the next phase – the markdown phase.
Markdown Phase: Panic and Despair
The markdown phase is characterized by:
A sustained downtrend in prices
Increased selling pressure
Panic selling by investors who bought assets during the distribution phase
Fear of further losses
Lower prices
Market sentiment shifting from uncertainty to outright fear
As prices continue to fall, despair sets in among investors. The fear of irreversible losses and the uncertainty of what lies ahead can cause investors to act irrationally, selling assets at significantly lower prices. However, savvy investors who understand market cycles know that this phase, like all others, is temporary and represents an opportunity to buy assets at discounted prices.
Recognizing Emotional Triggers in Market Cycles

For any investor, the skill of recognizing emotional triggers in market cycles can prove to be a valuable asset. A comprehension of these triggers can help investors maintain a rational stance towards investing and reduce the influence of market psychology on their decisions. Two key emotional triggers that can significantly influence market behavior are media influence and herd mentality.
Media, including news and social media, can significantly sway market sentiment. News can elicit bullish or bearish sentiment, influencing widespread buying or selling decisions. Similarly, herd mentality, the tendency of investors to follow the crowd rather than make independent decisions, can amplify market trends and contribute to the formation of asset bubbles or market crashes.
Media Influence and Sentiment Shifts
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping market sentiment and driving market movements. News announcements can directly impact investor trading behavior, while the emotional tone of media coverage can sway stock prices. For instance, positive news can trigger buying behavior, pushing prices higher, while negative news can induce selling, leading to price declines.
Shifts in media sentiment can significantly affect market psychology and influence market direction. For example, a surge in positive news can cause market euphoria, driving prices higher, while a wave of negative news can trigger market fear, leading to price declines. Recognizing these sentiment shifts can help investors make more informed investment decisions.
Overconfidence and Herd Mentality
Overconfidence and herd mentality are two cognitive biases that can significantly influence investor behavior. It can lead investors to overestimate their abilities and underestimate risks, leading to excessive trading and inadequate diversification. On the other hand, herd mentality can lead investors to follow the crowd, often resulting in irrational decision-making.
For example, during a bull market, overconfidence can lead to irrational exuberance, with investors piling into stocks without proper analysis. Similarly, herd mentality can lead to market bubbles, with investors buying assets simply because everyone else is doing so. Recognizing and mitigating these biases can help investors make more rational and informed decisions.
Tools for Monitoring Market Psychology

To make informed investment decisions, it is crucial to monitor market psychology. Various tools can help investors gauge the emotional state of the market and predict potential future trends. These tools include sentiment analysis tools and technical indicators.
By analyzing text data like news articles and social media posts, sentiment analysis tools can assist investors in understanding the overall mood of the market. Alternatively, an analysis of price action trends and patterns using technical indicators can help investors understand the market’s current emotional state.
If you would like to read more on real estate psychology, see our blog: https://www.quickcommissionadvance.com/blog/real-estate-psychology-unlocking-the-buying-and-selling-process/
Sentiment Analysis Tools
Sentiment analysis tools provide valuable insights into the overall mood of the market. These tools analyze digital text to determine the emotional tone of the message, categorizing it as positive, negative, or neutral. By analyzing patterns in text data, such as product reviews or social media posts, these tools can provide valuable insights into market sentiment.
Several sentiment analysis tools are commonly used in the stock market, including Digimind, and the stock market sentiment tracker. Though the accuracy of these tools may vary, they can offer valuable insights into market sentiment and help predict diverse stock trends.
Technical Indicators Reflecting Market Sentiment
Technical indicators, which are a type of technical analysis tools, serve as another beneficial tool in evaluating market sentiment. These indicators, such as the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), the High-Low Index, and the Bullish Percent Index (BPI), can provide insights into the overall emotions of market participants by analyzing price action trends and patterns.
For instance, the Fear and Greed Index can help investors understand the current emotional state of the market by signaling extreme fear or extreme greed. Similarly, the Put/Call ratio can indicate growing bearish sentiment in the market when the ratio surpasses 0.7 or goes beyond 1. Understanding these indicators can help investors make better-informed decisions.
Strategies for Navigating Emotional Market Cycles

The task of navigating emotional market cycles can pose a challenge. Despite this, investors can effectively weather these cycles by developing a robust strategy and practicing emotional discipline. Two key strategies that can help investors navigate emotional market cycles are developing a long-term investment plan and practicing emotional discipline.
Investors can maintain focus on their investment goals and evade impulsive decisions stemming from short-term market fluctuations with the help of a long-term investment plan. Alternatively, adopting emotional discipline can assist investors in maintaining a rational approach towards investing, thereby avoiding impulsive reactions to market news or price movements.
Developing a Long-Term Investment Plan
Developing a long-term investment plan is a crucial strategy for navigating emotional market cycles. A successful long-term investment strategy should include the following:
Align investments with objectives
Diversify across various investments
Refrain from market timing
Establish a systematic investment plan
Stay well-informed
Maintain consistency in the approach
In addition, understanding one’s risk tolerance is essential for developing a successful long-term investment strategy. Risk tolerance determines the level of risk an investor is willing to bear and influences the selection of investments and asset allocation. A long-term investment plan can help investors maintain focus during volatile market conditions and reduce the impact of market cycles.
Practicing Emotional Discipline
Practicing emotional discipline is another crucial strategy for navigating emotional market cycles. Emotional discipline involves maintaining composure and rationality amidst market fluctuations, refraining from impulsive decisions, and mitigating risk. By practicing emotional discipline, investors can make more logical and well-informed investment decisions.
Practicing emotional discipline involves setting clear entry and exit points, avoiding overreaction to market news, and maintaining a rational approach to investing. By recognizing emotional triggers and maintaining discipline, investors can navigate market cycles more effectively and make better investment decisions.
Summary
Understanding and navigating emotional market cycles is a crucial skill for any investor. By recognizing the emotional triggers that influence market cycles, using tools to monitor market psychology, and developing strategies such as a long-term investment plan and practicing emotional discipline, investors can make more informed and rational investment decisions. Remember, the key to successful investing lies not only in understanding the markets but also in understanding oneself.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the psychology of the market cycle?
The psychology of the market cycle is driven by the emotions and sentiments of its participants, leading to fluctuations in asset prices. Investor sentiment, including fear, greed, and euphoria, influences market movements and contributes to boom and bust cycles.
What is the psychology of the stock market?
The psychology of the stock market is influenced by human emotions such as pride, hope, greed, and fear, which can lead to common investing mistakes. Emotions and sentiments of market players can affect overall market trends, impacting buying and selling decisions.
What are the four phases of a market cycle?
The four phases of a market cycle are the accumulation phase, markup phase, distribution phase, and markdown phase. These phases are defined by specific investor emotions and behaviors, shaping market behavior and price movements.
What is the role of fear and greed in market cycles?
Fear and greed play a significant role in market cycles, as they are the primary emotions driving market sentiment, leading to fluctuations in prices.
How can sentiment analysis tools help investors?
Sentiment analysis tools can help investors by analyzing digital text to determine the emotional tone of the message, thus providing valuable insights into market sentiment. This can assist investors in making more informed decisions.







